API Authentication
Essential knowledge
Intended Audience:
Technical User
Authors:
Christopher Tse, Oliver Caine, Robert Wave, Girish Padmanabha
Changed on:
28 Jan 2026
Overview
APIs use authorization to ensure that client requests access data securely. This involves authenticating the sender of a request and verifying that they have permission to access or manipulate the relevant data. The authentication request returns a bearer token that can be used in subsequent API calls to confirm authentication.This guide covers the complete OAuth 2.0 authentication flow, including credential management, token lifecycle, and security best practices for production environments.Key points
- Token lifecycle management - Understand how to handle access tokens, refresh tokens, and expiration scenarios
- Security best practices - Form data submission is recommended over query strings for credential protection
- Integration options - Choose between standard client and FLUENT_INTEGRATION client based on your needs
- Error handling - Refresh tokens are single-use; implement proper fallback strategies
Authentication
APIs use authorization to ensure that client requests access data securely. This involves authenticating the sender of a request and verifying that they have permission to access or manipulate the relevant data.Bearer Token
The authentication endpoint returns a bearer token that can be used in the header of subsequent API calls to confirm authentication and maintain secure access.Authentication Flow
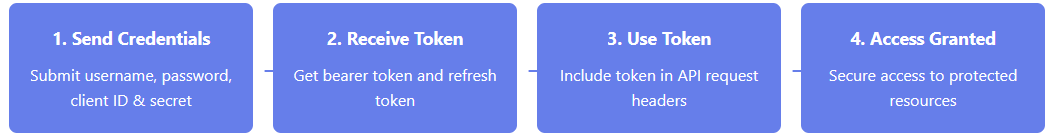
Token Lifecycle Diagram
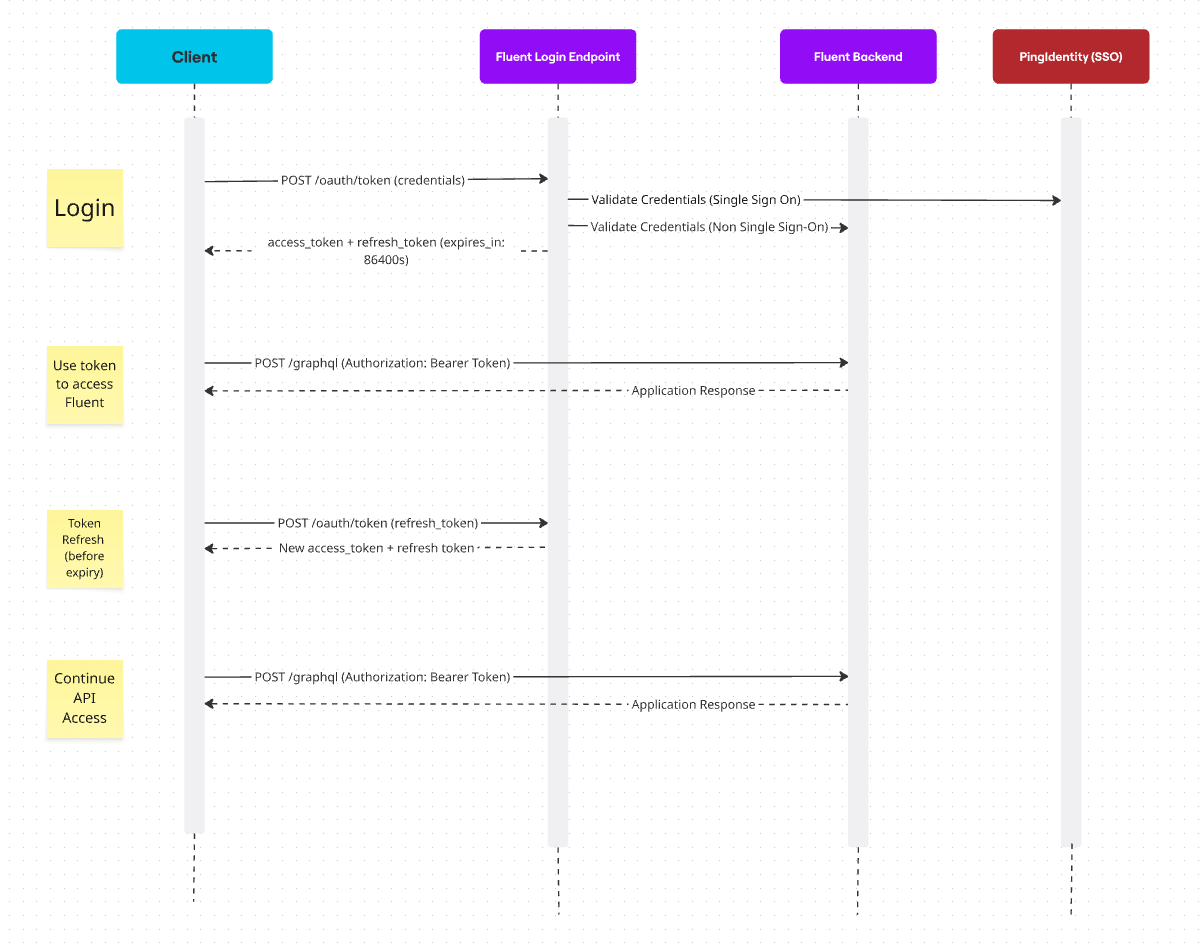
OAuth 2.0 Architecture
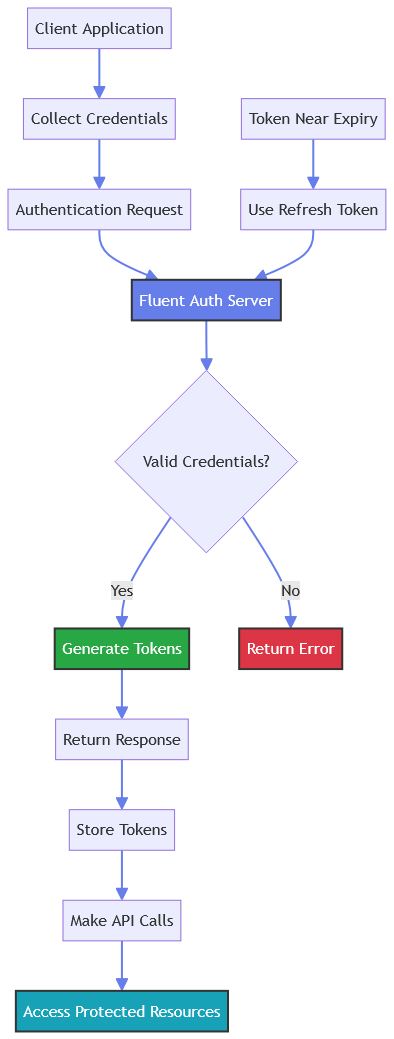
API Specifications
Technical details and endpoint configuration| Property | Value |
| URL | `<root_url>/oauth/token?<API Credentials>` |
| Methods | `POST` |
| Scheme | `https` |
| Content-Type | `See parameter submission methods below` |
| Headers | `fluent.account: <ACCOUNT_ID> ` |
Operations
Available authentication endpoints and methodsAPI CredentialsThe customer/partner will receive an email from Fluent Commerce that will contain the following information:
| Name | Multiple? | Description |
| API Key | ❌ No | This API key is to be used in the Store Locator and other Javascript widgets |
| API Client ID and secret | ❌ No | The API Client grants the retailer access to the content via the Fluent REST API. Each retailer will have one API Client |
Parameter Submission Methods
Recommended approaches for sending authentication parameters| Method | Content-Type | Security Level | Recommended | Notes |
| Form Data (POST Body) | `application/x-www-form-urlencoded` | 🟢High | ✅ Yes | Parameters hidden in request body |
| Query String | `application/json` or omit | 🔴Medium | ⚠️ Supported but not recommended | Parameters visible in URL |
Form Data Example
1POST /oauth/token HTTP/1.1 Host: ACCOUNT.sandbox.api.fluentretail.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded username=fluent-api&password=fluent-staging&scope=api&client_id=fluent-api&client_secret=ca5ce9a8-2f2e-4b4a-b8da-767f79fc81a9&grant_type=passwordResponse Codes
HTTP status codes and their meanings| Code | Description |
| 200 - Success | Successful Operation |
| 400 - Bad Request | Client Error - Bad Request |
| 401 - Unauthorized | Authorization Error - Invalid Bearer Token / No permission |
| 403 - Forbidden | Authorization Error - Forbidden |
| 404 - Not Found | Client Error - Not Found |
| 500 - Server Error | Server Error |
Example Requests
Practical examples of authentication requests and responsesStandard Authentication Request
Recommended: Form Data Method
1POST /oauth/token HTTP/1.1 Host: ACCOUNT.sandbox.api.fluentretail.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded username=fluent-api&password=fluent-staging&scope=api&client_id=fluent-api&client_secret=ca5ce9a8-2f2e-4b4a-b8da-767f79fc81a9&grant_type=password fluent.account: ACCOUNT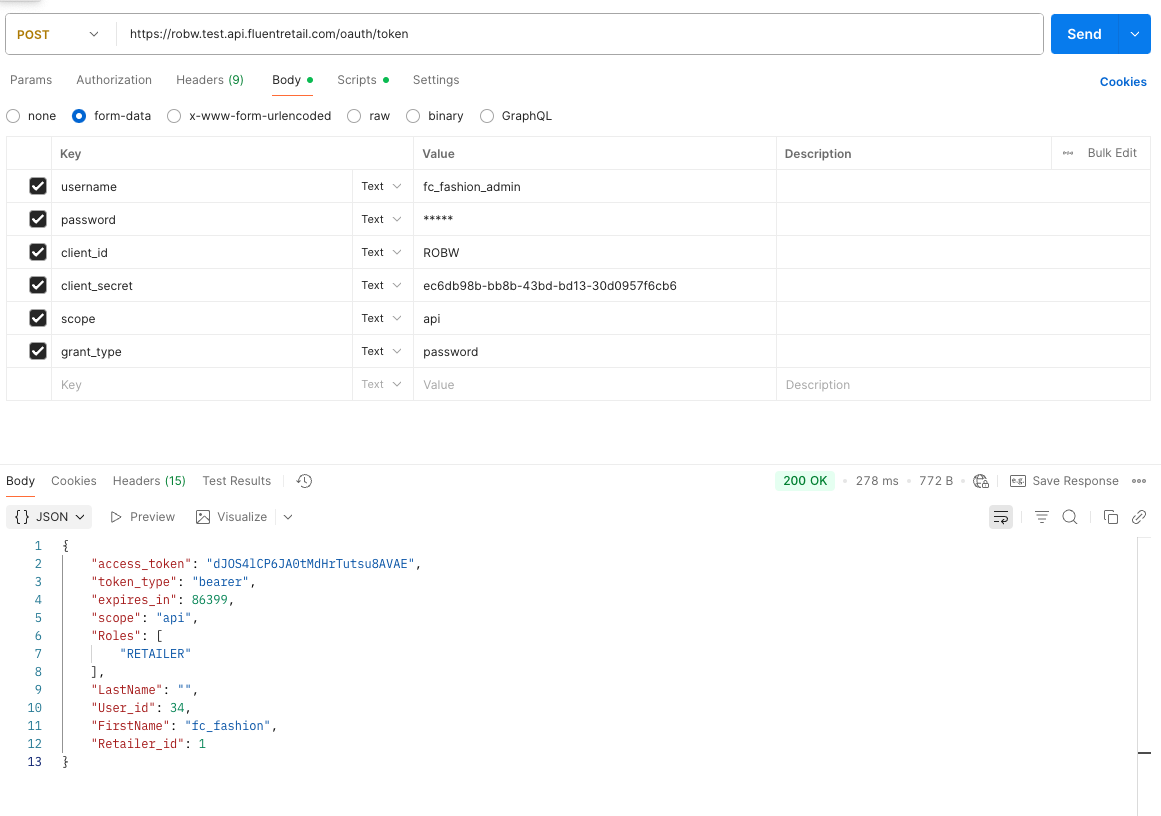
Alternative: Query String Method
1POST /oauth/token?username=fluent-api&password=fluent-staging&scope=api&client_id=fluent-api&client_secret=ca5ce9a8-2f2e-4b4a-b8da-767f79fc81a9&grant_type=password HTTP/1.1 Host: ACCOUNT.sandbox.api.fluentretail.com Content-Type: application/json fluent.account: ACCOUNT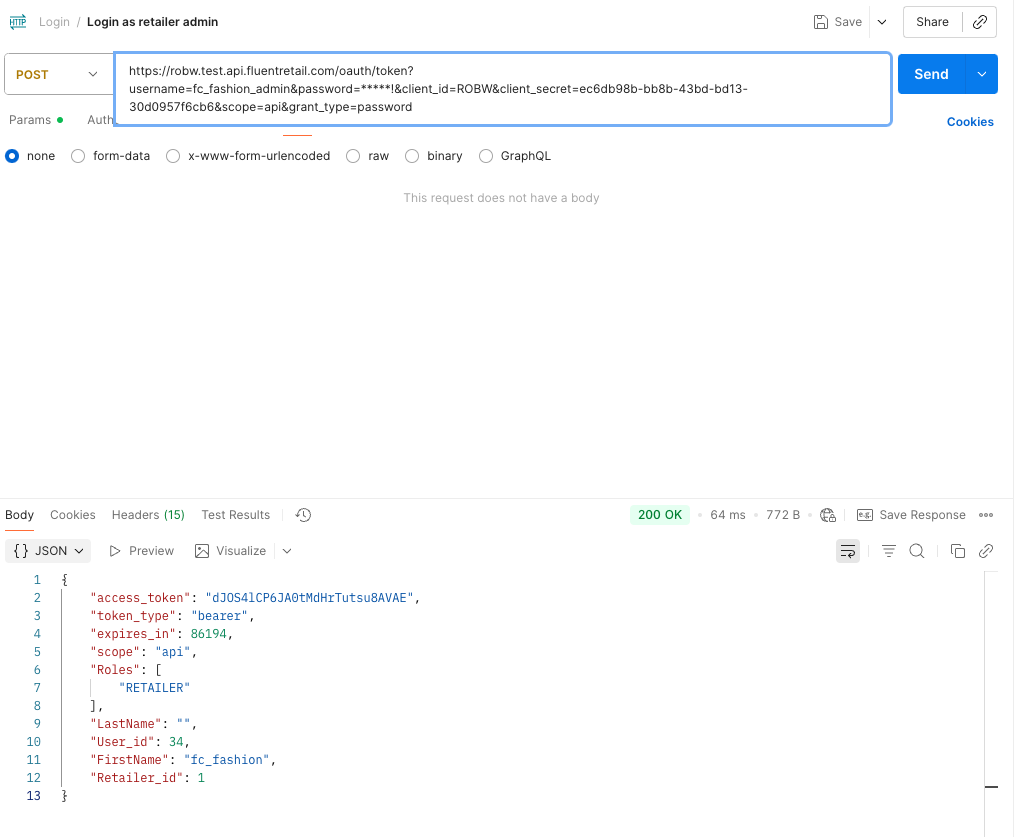
Success Response:
1{
2 "access_token": "cf02e220-86ea-408d-9b80-fb55f517725b",
3 "token_type": "bearer",
4 "refresh_token": "xlUuQ5e-h9Y2pRw5G4Du4fAdRfk",
5 "expires_in": 86386,
6 "scope": "api",
7 "Retailer_id": 1,
8 "FirstName": "Fluent",
9 "LastName": "Commerce",
10 "Roles": []
11}Error Response:
1{
2 "errors": [
3 {
4 "code": "400",
5 "message": {
6 "error": "invalid_grant",
7 "error_description": "Bad credentials"
8 }
9 }
10 ]
11}FLUENT_INTEGRATION Client Request
Integration Users - users for the FLUENT_INTEGRATION client id - have a short-lived token authentication flow. These users are set up with short-lived access tokens (30 minutes / 1800 seconds by default) and are issued a refresh token. This refresh token can be used with the login endpoint endpoint to renew authentication without sending a username and password. A shorter expiry time enhances security by ensuring that any tokens issued are not valid for longer than necessary, and the refresh token allows integrations to stay authenticated without continuously sending sensitive credentials to Fluent.Refresh tokens issued for FLUENT_INTEGRATION client types expire after 24 hours / 86400 secondsRecommended: Form Data Method
1POST /oauth/token HTTP/1.1 Host: ACCOUNT.sandbox.api.fluentretail.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=FLUENT_INTEGRATION&scope=retailer&username=fluent-api&password=fluent-staging&client_secret=ca5ce9a8-2f2e-4b4a-b8da-767f79fc81a9&grant_type=password fluent.account: ACCOUNTAlternative: Query String Method
1POST /oauth/token?client_id=FLUENT_INTEGRATION&scope=retailer&username=fluent-api&password=fluent-staging&client_secret=ca5ce9a8-2f2e-4b4a-b8da-767f79fc81a9&grant_type=password HTTP/1.1 Host: ACCOUNT.sandbox.api.fluentretail.com Content-Type: application/jsonSuccess Response:
1{
2 "access_token": "O1ogEE-LnvZIp_c3DCgKXfhiJII",
3 "token_type": "bearer",
4 "refresh_token": "fx25qnHPXER80FUx-Qo9ce02ITs",
5 "expires_in": 1799,
6 "scope": "retailer",
7 "Retailer_id": 5,
8 "Roles": [
9 "RETAILER"
10 ],
11 "FirstName": "Fluent",
12 "LastName": "Commerce"
13}Refresh Token Request
An Authentication API request with the`username` and `password` parameters substituted with a `refresh_token`:Recommended: Form Data Method
1POST /oauth/token HTTP/1.1 Host: ACCOUNT.sandbox.api.fluentretail.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded refresh_token=zVusnPsE3dPjXEi4b1p6DYHoL8E&scope=api&client_id=fluent-api&client_secret=ca5ce9a8-2f2e-4b4a-b8da-767f79fc81a9&grant_type=refresh_token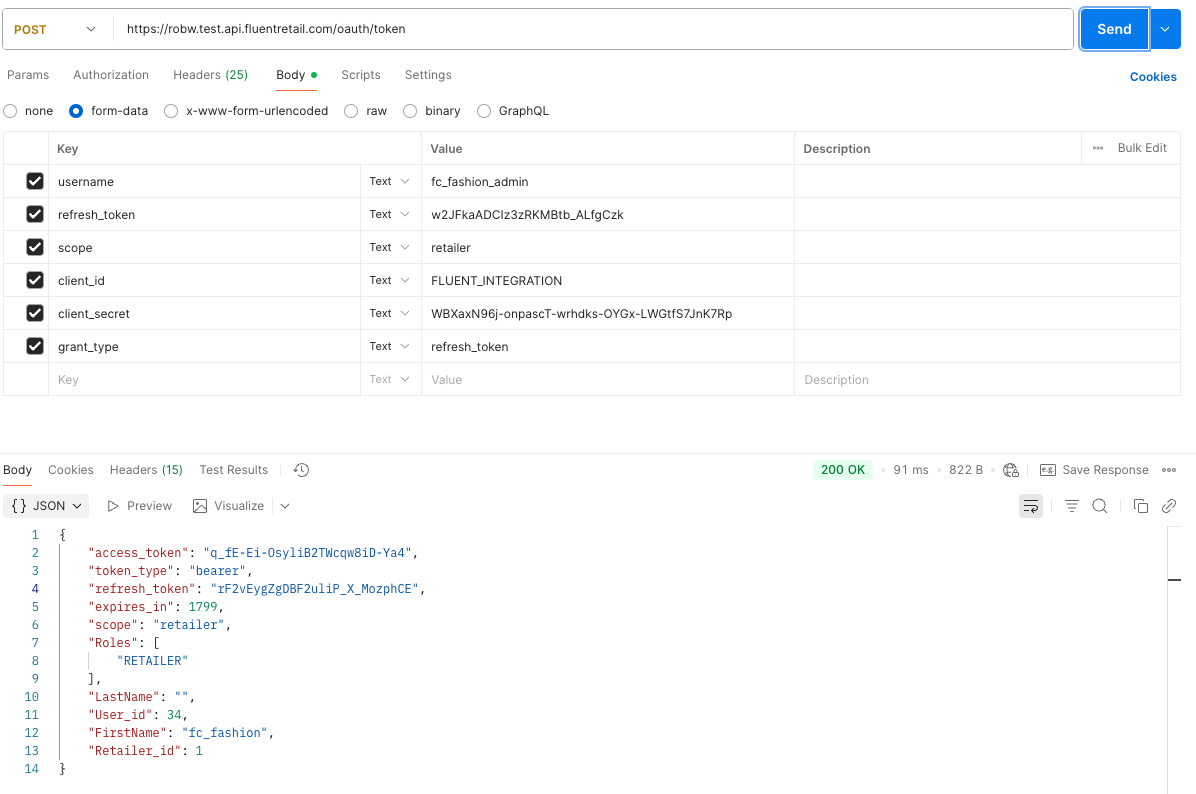
Alternative: Query String Method
1POST /oauth/token?refresh_token=zVusnPsE3dPjXEi4b1p6DYHoL8E&scope=api&client_id=fluent-api&client_secret=ca5ce9a8-2f2e-4b4a-b8da-767f79fc81a9&grant_type=refresh_token HTTP/1.1 Host: ACCOUNT.sandbox.api.fluentretail.com Content-Type: application/json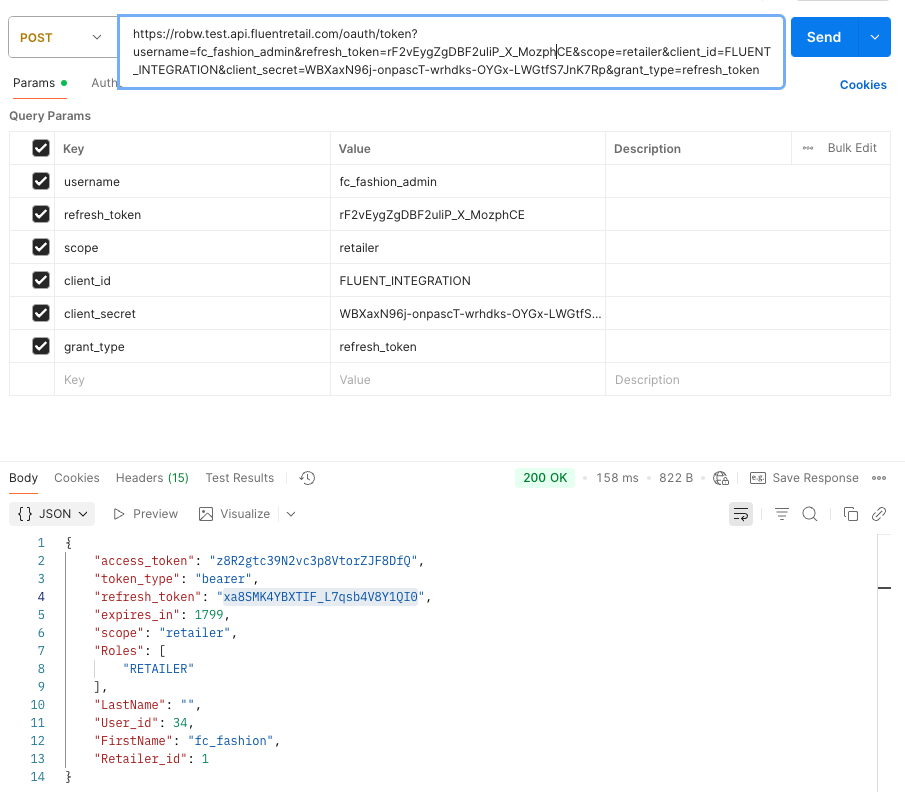
Usage in Mystique: Refresh tokens are currently used in Mystique to ensure a user remains logged in when they have a browser session open. The access token is checked every 30s to validate how much time is remaining until expiry. If the access token is close to expiring, the refresh token is automatically used to retrieve a new access token.
Understanding Response Objects
When you receive a successful authentication response, each field serves a specific purpose:`access_token`
Purpose: Your main authentication credential for API calls.Usage: Include this in the Authorization header of all subsequent API requests.`Authorization: Bearer cf02e220-86ea-408d-9b80-fb55f517725b`Security: Store securely, never expose in client-side code or URLs.`token_type`
Purpose: Specifies the type of token (typically "bearer").Usage: Use this value in the Authorization header format.`expires_in`
Purpose: Number of seconds until the access token expires.Usage: Calculate expiration time and implement token refresh logic before expiry.Example: If expires_in is 86386 seconds (≈ 24 hours), refresh the token 5-10 minutes before expiration.`refresh_token`
Purpose: Used to obtain new access tokens without re-authentication.Usage: Store securely and use when access token is near expiration.`scope`
Purpose: Defines the level of access granted (e.g., "api", "retailer").Usage: Determines which API endpoints and operations you can access.`Retailer_id, FirstName, LastName, Roles`
Purpose: User and account context information.Usage: Use for personalization, authorization checks, and audit logging.Token Lifecycle Management
Proper token management is crucial for maintaining secure and uninterrupted API access.1. Initial Authentication
Store both access_token and refresh_token securely. Calculate expiration time using expires_in value.2. Token Usage
Use access_token in Authorization header for all API calls. Monitor token expiration time.3. Proactive Refresh
Refresh token 5-10 minutes before expiration to avoid service interruption.4. Handle Expiration
If you receive 401 Unauthorized, immediately attempt token refresh or re-authentication.Models
Data structures for requests and responsesResponse Model
| Key | Type | Required | Description |
| access_token | String | ✅ | The access token string as issued by the authorization server |
| token_type | String | ✅ | The type of token. This will typically be the string “bearer” |
| expires_in | Integer | ❌ | If the access token expires, this field will return a value in seconds until the token expires |
| scope | String | ❌ | The scope of the access token |
| refresh_token | String | ❌ | Refresh tokens can be used to fetch a new access token without needing username and password |
| Retailer_id | Integer | ❌ | This is a unique ID associated with the retailer |
| Roles | [String] | ❌ | An array of the Roles associated with the returned token |
| FirstName | String | ❌ | The first name of the user account that requested the token |
| LastName | String | ❌ | The last name of the user account that requested the token |
Error Model
| Key | Type | Possible Values | Description |
| errors | Array | - | List of errors |
| code | String | 400, 401, 403, 404, 500 | error code |
| message | String | - | description of the error |

