GraphQL Query Limits
Authors:
Fluent Commerce, Kirill Gaiduk
Changed on:
25 Sept 2024
Overview
The following guidelines and specifications apply to the entire schema, with any exceptions documented in the schema of the relevant entity.Key points
- The GraphQL request size is limited to 2MB
- There is no validation on any of the GraphQL fields (except for enums)
- The GraphQL query complexity is limited and checked in accordance with the Query Complexity Calculation Algorithm (11,111 Total Complexity is Max)
General Guidelines
The request size is limited to`2MB`. Requests over `2MB` will return `HTTP 413 Request Entity Too Large` response.The number of attributes is not limited; however, it is important to note that storing many attributes is not considered best practice. While the underlying storage capacity of JSON allows for up to 255MB to be allocated, it is recommended to avoid excessive attributes as they can adversely impact performance and potentially result in errors.Wherever there's no specific `maxLength` of a String defined, 255 characters is the default.There's no hard-coded validation on any of the GraphQL fields (except for `enums`). For example, these include (not a comprehensive list):- OrderItemStatus
- FulfilmentItemStatus
- CardType
- LocationType
Data Retrieval
A key benefit of GraphQL is that users can send a single request to retrieve data from various sources.While this is great for developer experience, it does add additional load on the server when an advanced GraphQL query could potentially create tens of thousands of queries to be executed by the backend. Fluent Commerce have therefore added query complexity checks to the GraphQL API. These checks ensure the API remains stable and maintains speed and efficiency.GraphQL Query Complexity
For each GraphQL query, the platform calculates the complexity of the query based on the number of possible database operations. If the complexity is high, the platform will block the request and advise the user to query again with a lower complexity query. This prevents the server from attempting to execute superfluous requests that will most likely time out.- Clients can supply a first or last argument on any connection. If the first and last are not provided, the default argument is the first 10.
- Values of first and last should be within 1 - 5,000. If the first or last is greater than 5,000, it will be reset to 5,000. This means that the page size limit has been increased from 100 to 5000.
- Individual requests with a complexity more than 11,111 will result in error code C10001E being displayed.
Query Complexity Calculation Algorithm
The general principle is that Total Complexity equals the number of queries to be executed.Simple Query

Complexity Calculation

Complex Query
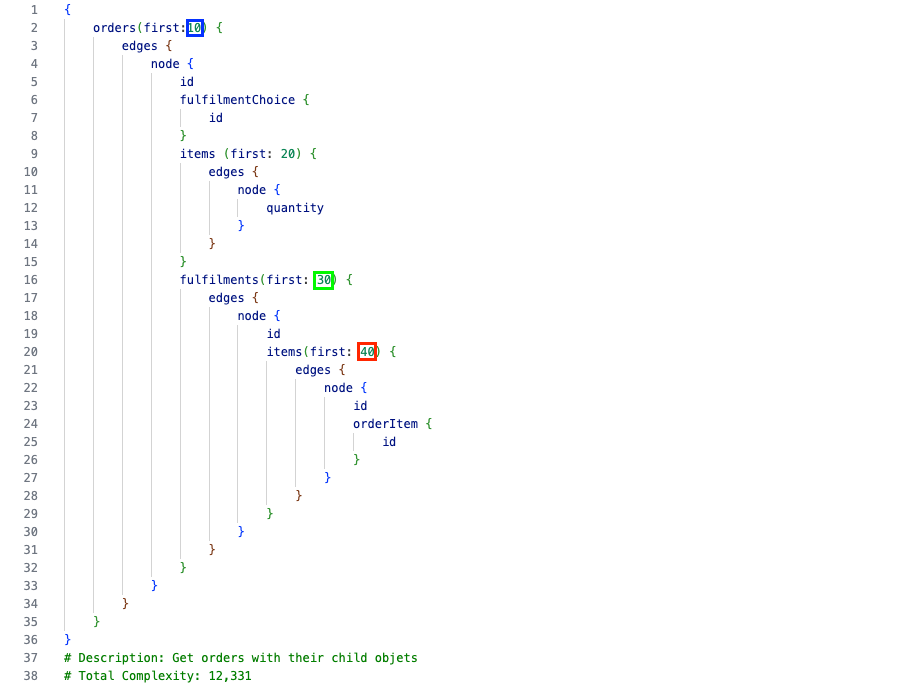
Complexity Calculation

Query with Weighting
Some GraphQL queries have an increased complexity weighting, determined by a`@complexityCost` directive in the GraphQL schema. This directive assigns a weighting factor to specific queries, which multiplies the query's complexity result by the specified value.The key purpose of complexity weighting is to reduce the risk of an API timing out.Inventory Quantity Aggregations
The complexity weighting of`10` is used for the Inventory Quantity Aggregation queries (`quantitiesAggregate`).If the Inventory Quantity Aggregation is encountered within the supplied GraphQL query, then the resulting node complexity is multiplied by the weight (x10).
Complexity Calculation

