Getting Started with Reference Sourcing Criteria
How-to Guide
Author:
Kirill Gaiduk
Changed on:
26 Sept 2025
Key Points
- Understand the Ranking Mechanism: Sourcing Criteria score (or exclude) candidate Locations to drive ranking and tie-breaking
- Sequence Matters: Criteria are evaluated top-to-bottom; the first Criterion decides the primary order, the next acts as a tie-breaker
- Normalize Ratings: Most Criteria return raw numeric ratings that the framework normalizes across Locations to ensure consistent comparisons
- Use Exclusion Carefully: Some Criteria return a negative score (-1) to exclude Locations; apply these early in the stack for predictable outcomes
- Know When to Extend: The reference library covers common distance, inventory availability, and priority logic; develop a custom Criterion for domain-specific logic
Prerequisites
Steps
 Core Concept
Core Concept
A Sourcing Criterion is a configurable function that evaluates a candidate Location in context of the Sourcing Request and returns a rating:
- A positive float (0…1) ranks how suitable a Location is
- -1 filters a Location out of consideration
- Criteria are applied in sequence to produce a final ranked list of eligible Locations
`type` (for example, `fc.sourcing.criterion.locationDistance`) and applies its `apply()` method to every candidate Location. Internal Mechanics
Internal Mechanics
Reference Criteria share common behavior through
`BaseSourcingCriterion` and Criterion Utilities:- Apply → Execute → Normalize:
`apply()`calls pre-logic, executes business rules, and post-logic`normalize()`adjusts raw scores to a [0–1] range where applicable
- Sequential Stack:
- Criteria are applied in order of appearance
- The first Criterion usually defines the main ranking dimension (e.g., distance or inventory availability)
- Later Criteria resolve ties
- Parameter Parsing:
`parseParams()`reads JSON params defined in the`fc.rubix.order.sourcing.criteria`Setting- Helper Utilities (
`getFloats`,`getStrings`,`getDistanceUnits`) ensure correct types and default handling
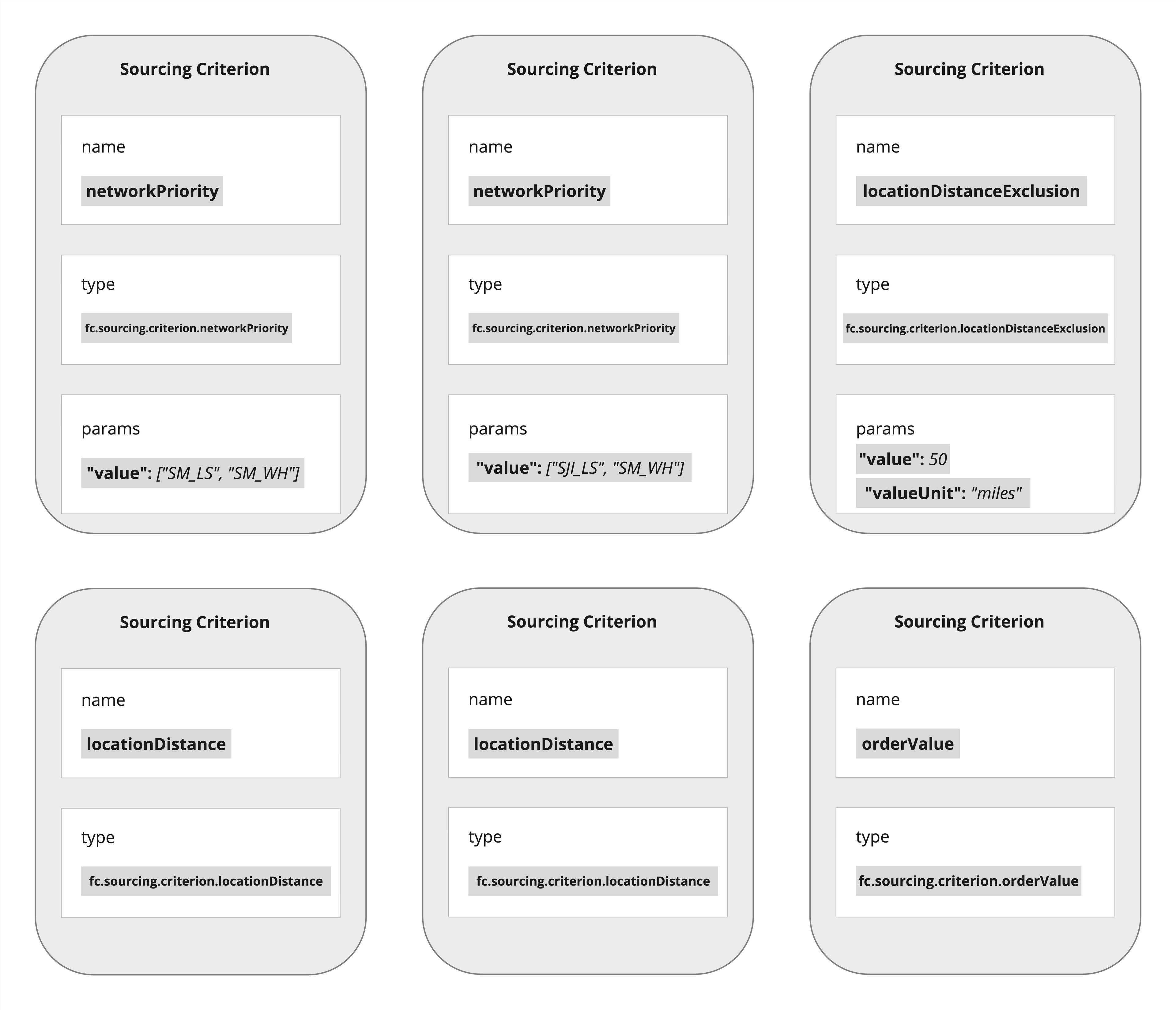
 Reference Sourcing Criterion Functions
Reference Sourcing Criterion Functions
| Class(Criterion Utilities) | Type(Sourcing Criteria Schema) | Description(UI) | Notes |
`LocationDistanceCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.locationDistance` | Prioritises locations that are geographically closer to the delivery address |
|
`LocationDistanceBandedCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.locationDistanceBanded` | Ranks locations by distance bands {{value}}, prioritising bands that are closer |
|
`LocationDistanceExclusionCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.locationDistanceExclusion` | Excludes locations that are farther than {{value}}{{value}} | Excludes (-1) Locations beyond a specified maximum distance threshold (in km or miles) |
`LocationDailyCapacityCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.locationDailyCapacity` | Prioritises locations with the highest available daily fulfillment capacity | Rates Locations based on their `DAILY_MAX_ORDER_CAPACITY` attribute value (higher capacity = higher rating) |
`NetworkPriorityCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.networkPriority` | Prioritises locations by the specified network ranking {{value}} |
|
`InventoryAvailabilityCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.inventoryAvailability` | Prioritises locations based on total units of inventory requested in the order that can be fulfilled |
|
`InventoryAvailabilityBandedCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.inventoryAvailabilityBanded` | Ranks locations by fulfillment percentage bands {{value}}, prioritising bands with higher availability |
|
`InventoryAvailabilityExclusionCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.inventoryAvailabilityExclusion` | Excludes locations where inventory availability for a given order, is less than {{value}}% | Excludes (-1) Locations that do not meet the configured minimum fulfillment threshold (in %) |
`LocationTypeExclusionCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.locationTypeExclusion` | Excludes locations of type {{value}} | Excludes (-1) Locations whose type matches a configured value(s) (e.g., store vs. warehouse) |
`LocationNetworkExclusionCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.locationNetworkExclusion` | Excludes locations that are members of one of the following networks {{value}} |
|
`OrderValueCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.orderValue` | Prioritises locations that fulfill a higher monetary portion of the order |
`InventoryAvailabilityCriterion`, surplus Inventory does not increase the score above 1 because the calculation caps the fulfilled value at the requested quantity of each Item |
Default Sourcing Criteria
| Class | Type | Notes |
`RejectedLocationExclusionCriterion` | `fc.sourcing.criterion.locationExclusion` | Automatically excludes Locations that previously rejected Items in the same Sourcing Request (applied by default, not shown in UI) |
 Parameter Definitions
Parameter Definitions
Sourcing Criteria rely on parameters defined in the
`fc.rubix.order.sourcing.criteria` Setting to ensure valid configuration:`value`: Numeric thresholds or band breakpoints. An input like [10, 25, 50] defines 4 bands:- (–∞ … 10]
- (10 … 25]
- (25 … 50]
- (50 … +∞)
`valueUnit`: Selects unit of measure where applicable (kilometres, miles)`component`: UI input type such as`fc.field.multistring`,`integer`, or`select``mandatory`/`exactSearch`: Validation flags controlling whether the field must be provided and if exact match applies
 Configuration in the UI
Configuration in the UI
The reference schema in
`fc.rubix.order.sourcing.criteria` Setting defines templates for all reference Sourcing Criteria. Each template specifies the required UI components and their validation rules to ensure that Criteria parameters are entered consistently and correctly.For account/retailer-specific adjustments, override Criteria in `fc.rubix.order.sourcing.criteria.custom`. When a Criterion with the same `name` exists in both schemas, the custom schema takes precedence, allowing organizations to tailor global definitions to their own business needs without breaking the baseline. Attaching Criteria to Strategies
Attaching Criteria to Strategies
Sourcing Criteria are added to Primary or Fallback Sourcing Strategies via the Sourcing Profile GraphQL API, similar to Conditions.
 Best Practices
Best Practices
- Order Criteria deliberately: put Exclusion Criteria first, then your primary ranking Criterion, then tie-breakers
- Provide exact values and enforce strict types via schema-driven components (e.g., units in select, numeric bands)
- Test boundary and edge cases thoroughly
- Apply overrides in
`fc.rubix.order.sourcing.criteria.custom`when tailoring Criteria for specific Accounts / Retailers

