What are Fluent OMS Entities? (Entity)
Essential knowledge
Intended Audience:
Technical User
Authors:
Agnes Schliebitz-Ponthus, Cille Schliebitz, Randy Chan
Changed on:
5 Sept 2025
Overview
A detailed explanation of Fluent OMS entities and how they can be used throughout the order journey.Key points
- Entities in Fluent OMS are data objects that store and process information throughout the order journey, such as orders, fulfilments, and financial transactions.
- Entities are managed via GraphQL, with mutations and queries used to create, update, and retrieve entity data.
- Entities should not be deleted but controlled using status fields, although some "remove" mutations can disconnect entities.
- Orchestrated Entities trigger a CREATE event upon successful creation, enabling workflow automation.
- Entities in Fluent OMS serve unique purposes to enable an end-end digital commerce journey and their statuses determine at what stage they sit.
- Entities have types and subtypes, types are rigidly defined, subtypes are more flexible.
What are Entities?
The entity is a data object that can store and process data. For example, an order entity stores customer order-related information as an object within OMS, and the order entity data can be used or processed later in the order journey.Each entity contains a defined set of fields and connections for storing the relevant data. For example, an`order->type` declares the order type as HD or CC and can link to zero or more fulfilments by using `order->fulfilments`. Most transactional entities typically have a status field to represent their current state. (e.g. `BOOKED`, `CANCELLED`, `COMPLETE`)Most transactional entities have attribute fields available where users can use attributes to store specific values that can be used for the downstream workflow. What do you need to know about Entities?
The Entity is accessible by using GraphQL. Using Order as an example again, the`createOrder` mutation creates an Order entity, `updateOrder` mutation updates the existing order entity, and `orderByID` or `orders` queries retrieve the Order data.Removing Entities
As a SaaS platform, entities cannot (should not) be deleted in OMS. Typically, the user should use the status field to control the entity's functionality. However, some "remove" mutations allow the user to remove the connection between entities, whereas update mutations cannot remove the connections for certain entities—for example,`removeNetworkFromLocation`, `removePermissionsFromRole`. More mutations can be found via the GraphQL API Explorer or the Reference Schema.Orchestratable Entity
The orchestratable entity is an entity whose life cycle can be orchestrated by a workflow. This means the different status this entity can be in, and any update of the entity should be done via its workflow. The list of Orchestratable Entities can be found in the GraphQL Orchestrateable Reference.Here is an example of the
`OrderCancel` ruleset getting orchestrated within the HD workflow.1[{
2 "name": "OrderCancel",
3 "description": "Cancels order",
4 "type": "ORDER",
5 "subtype": "HD",
6 "eventType": "NORMAL",
7 "rules": [
8 {
9 "name": "{ACCOUNTID}.core.SetState",
10 "props": {
11 "status": "CANCELLED"
12 }
13 },
14 {
15 "name": "{ACCOUNTID}.order.SendEventForAllFulfilments",
16 "props": {
17 "eventName": "CancelFulfilment"
18 }
19 }
20 ],
21 "triggers": [
22 {
23 "status": "CREATED"
24 },
25 {
26 "status": "RECEIVED"
27 },
28 {
29 "status": "BOOKED"
30 }
31 ],
32 "userActions": [
33 {
34 "context": [
35 {
36 "label": "CANCEL ORDER",
37 "type": "PRIMARY",
38 "modules": [
39 "adminconsole"
40 ],
41 "confirm": true
42 }
43 ],
44 "attributes": []
45 }
46 ]
47},
48{
49 "name": "CancelFulfilment",
50 "description": "Cancels all the fulfilments when the order is cancelled,sends an event to inventory catalog to reset any reserved inventory against the fulfilment",
51 "type": "FULFILMENT",
52 "eventType": "NORMAL",
53 "rules": [
54 {
55 "name": "{ACCOUNTID}.order.CancelFulfilment",
56 "props": null
57 },
58 {
59 "name": "{ACCOUNTID}.order.SendEventToUpdateInventoryQuantity",
60 "props": {
61 "eventName": "UpdateInventoryQty",
62 "operation": "UNRESERVE",
63 "retailerId": "5000299",
64 "inventoryCatalogueRef": "DEFAULT:5000299"
65 }
66 }
67 ],
68 "triggers": [
69 {
70 "status": "CREATED"
71 },
72 {
73 "status": "PROCESSING"
74 },
75 {
76 "status": "AWAITING_WAVE"
77 }
78 ],
79 "userActions": []
80}
81]`OrderCancel` ruleset:1POST: {{fluentApiHost}}/api/v4.1/event/async
2
3{
4 "name": "OrderCancel",
5 "accountId": "{ACCOUNTID}",
6 "retailerId": "5000299",
7 "rootEntityRef": "HD_789535507",
8 "rootEntityType": "ORDER",
9 "entityRef": "HD_789535507",
10 "entityType": "ORDER",
11 "attributes": {
12 "CANCEL_REASON": "CREDIT FAILED"
13 }
14}
15
16
17`OrderCancel` ruleset. The `OrderCancel` ruleset executes two rules to set the order status to CANCELLED and send an event to the `CancelFulfilment` ruleset for every fulfillment. The `CancelFulfilment` ruleset cancels the fulfillment and un-reserves the quantities. Hence, orchestrate entities update via EVENT API call is much more efficient than by calling GQL `updateOrder` mutationOrchestratable Entities that send a CREATE event
Here is the list of "Orchestratable Entity" if successfully created, will generate a CREATE event associated with the mutation:- Order
- Fulfilment
- Article
- Wave
- Fulfilment Option
- Fulfilment Plan
- Product Catalogue
- Standard Product
- Variant Product
- Category
- Inventory Catalogue
- Inventory Position
- Inventory Quantity
- Return Order
- Return Fulfilment
- Billing Account
- Credit Memo
- Invoice
- Payment
- Payment Transaction
Where do Fluent Commerce Entities fit in the Digital Commerce Journey?
Fluent Commerce's key domain entities serve unique purposes for different stages of the digital commerce journey. Workflows bring these entities and their purposes to life. The table below explains where each is used.Green cells indicate a direct relationship between an entity and that stage of the workflow, while light green cells indicate that the entity is only partially involved. For example, the`fulfilment` entity is only involved in payment processing at the invoicing stage as the 'Ready to Ship' status is directly linked to the `fulfilment` entity. 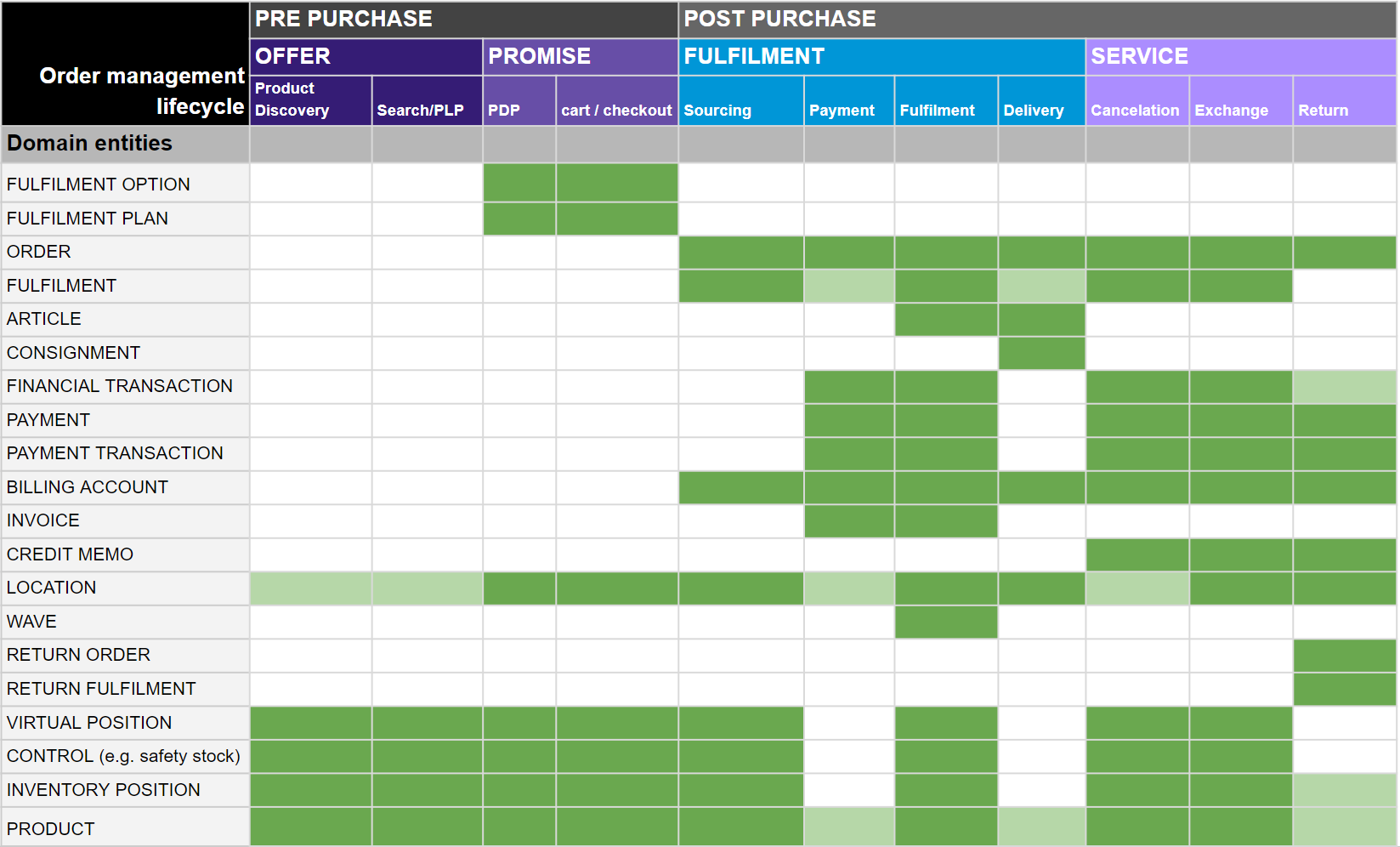 See the video below on how to look for statuses within a workflow, you can learn more about entities and their available statuses in the Fulfilment and Order reference modules.
See the video below on how to look for statuses within a workflow, you can learn more about entities and their available statuses in the Fulfilment and Order reference modules.