Fluent Connector Configuration
Essential knowledge
Author:
Fluent Commerce
Changed on:
20 Nov 2023
Overview
The Connect SDK expects a minimum of 4 configuration files:- application-connector.yml - Project and Connector specific configuration.
- application.yml - Core Connect SDK configuration. These are mostly default configurations and core settings.
- bootstrap.yml - Server/Container configuration. This file includes settings for all different environments and - follows the spring profile standards.
- logback-spring.xml - Log configuration also supports different configurations based on spring profiles.
Key points
- Credential / Secrets Configuration
- Configuration Service
- Listener Configuration
- Job Scheduler Configuration
- Cache Configuration
- Product Availability
- API Key Configuration
- Spring actuators
Credential / Secrets Configuration
For the Connect SDK to interact with external systems, it requires access to their credentials, which must be stored in a secured location. The SDK provides a way for new credential storage services to be added, which is covered in the customisation guide. The example below uses a credential service from the connect-sdk-core-aws module, and to configure your credentials on your development environment, follow the Credential / Secret Setup Guide.1fluent-connect:
2 credential:
3 credential-manager: "aws-secrets-manager"| Property | Required | Description | Default |
| credential-manager | yes | ID of the credential service used by the SDK. | n/a |
Basic SDK Secret Configuration
- Active accounts This is used to tell the SDK what region the account is on Fluent and what retailers the Connect SDK will consider when processing messages.
- sydney
- dublin
- singapore
- north_america
`fc/connect/{connector-name}/api/fluent/activeAccounts`Sample Configuration:1{
2"accounts": [
3 {
4 "name": "CNCTDEV",
5 "region":"sydney",
6 "retailers": [
7 1,
8 34,
9 67,
10 100
11 ]
12 }
13]
14}- Fluent Credentials
`fc/connect/{connector-name}/{your-fluent-account}/api/fluent-account/1`Sample Configuration:1{
2 "retailer": "1",
3 "userName": "<FLUENT-RETAILER-USERNAME>",
4 "password": "<FLUENT-RETAILER-PASSWORD>"
5}Custom Secrets
It is possible to store any secret at the secret manager and have the SDK use them. All secret names must adhere to the SDK naming convention; otherwise, they will be discarded and not used. All secrets must be prefixed with:`fc/connect/{connector-name}/`. An example of a custom secret is `fc/connect/{connector-name}/my-secret`.Configuration Service
The SDK uses a configuration service to read runtime configuration/settings. The default implementation uses Fluent settings as the storage location, but adding a new service to manage the runtime configuration/settings is possible.1fluent-connect:
2 configuration:
3 settings-manager: "fluent-settings"| Property | Required | Description | Default |
| settings-manager | yes | ID of the configuration service used by the SDK. The default setting uses Fluent Settings as the storage location. | `fluent-settings` |
General Configuration
Connect SDK provides the following configuration.| Property | Required | Description | Default |
| connector-name | yes | This is the connector's name and this property is used to both name the connector and build the path of other configuration keys. Keep characters limited to 'a-z' and '-'. | n/a |
| event-log-manager | no | Id of the service that will log SDK events. There are two pre-defined options:`fluent-eventlog`: writes events to the standard log output.`disabled`: does nothing when an event is requested to be tracked | `fluent-eventlog` |
| enable-listeners | no | Enable or disable all SDK listeners | true |
| disable-listeners | no | A list of handlers will be disabled. The routes that use these disabled handlers will be disabled as well Example: `disable-handlers: EventFailureSummaryJobHandler` | empty |
1connector-name: <my-connector-name>
2event-log-manager: "fluent-eventlog"| Property | Description | Default |
| base-path-key | Controls the base key path of all configurations of the SDK. Nothing outside the path is read by the SDK. When using the SDK to fetch a configuration, it is not required to specify the full path of the fluent setting. The SDK will automatically infer the full path based on this property. For example, requesting a configuration named “my-key” will result in the SDK retrieving “ `fc.connect.<my-connector-name>.my-key`” setting from Fluent. | `fc.connect.<my-connector-name>` |
| account-mapping-key | Maps a Fluent account-retailer to an external system. The identification of the external system must be unique, and it is possible to be a composite value. | `fc.connect.<my-connector-name>.account-mapping` |
| general-key | Any general settings that don't quite fit in any category. | `fc.connect.<my-connector-name>.general` |
| log-level-key | Global level setting key to controlling the SDK's log level (DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR). Changes to this property will take effect on the first configuration refresh in the SDK. | `fc.connect.<my-connector-name>.log-level` |
| unit-conversion-key | Used for unit conversion configuration, for example, Kilogram to Gram. | `fc.connect.<my-connector-name>.unit-conversion` |
Configuration Samples
1{
2 "fluent": {
3 "accountId": "FCTDEV",
4 "retailerId": "100"
5 },
6 "externalAccount": {
7 "projectKey": "my-project-qa",
8 "uid": "123"
9 }
10}1{
2 "productCatalogue": {
3 "entityRef": "PC:MASTER:100",
4 "entitySubType": "MASTER"
5 }
6}1{
2 "conversionSettings": [
3 {
4 "fromUnit": "cm",
5 "toUnit": "mm",
6 "conversionFactor": 10
7 },
8 {
9 "fromUnit": "kg",
10 "toUnit": "gm",
11 "conversionFactor": 1000
12 }
13 ]
14}1{
2 "fluent": {
3 "PROCESSING": "Initial",
4 "AWAITING_WAVE": "Initial",
5 "ASSIGNED": "picking",
6 "PARTIALLY_FULFILLED": "picking",
7 "FULFILLED": "picking",
8 "AWAITING_COURIER_COLLECTION": "readyToShip",
9 "AWAITING_CUSTOMER_COLLECTION": "readyToShip",
10 "COMPLETE": "shipped",
11 "ESCALATED": "Initial",
12 "REJECTED": "backorder",
13 "CANCELLED": "Cancelled"
14 }
15}Listener Configuration
Listeners allow connectors to subscribe to queues/topics which is enabled by default. To disable all listeners, including the SDK internal listeners, set the following property`enable-listeners: false` at application-connector.yml. It is possible to have any number of listeners running, and each must have its own configuration, like the sample below.1listeners:
2 # listener configuration block
3 listener-id:
4 name: "ENV_VARIABLE"
5 fluent-account: FLUENT_ACCOUNT
6 type: "sqs"
7 core-pool-size: 5
8 pool-size: 20
9 prefix: "my-prefix"
10 shutdown-timeout: 300
11 visibility-timeout: 120
12 poll-wait: 20
13 dlq-suffix: "-dlq"
14 retry: 5 | Property | Required | Description | Default value |
| listener-id | yes | Actual id of the listener. This must match the id defined at the class when using @ListenerInfo. | n/a |
| name | yes | Name of the environment variable that will contain the real queue name. | Empty String |
| type | yes | Type of listener. This is based on a list of supported listeners of the Connect SDK. Current options are: `sqs` or `kafka`.Notes: The required SDK library must be present to use different listener types. | NOT_DEFINED |
| fluent-account | required for custom queues (aka external queues) | Fluent account name. This is required and restricts the processing of messages to services and configuration for said account. | n/a |
| core-pool-size | no | Minimal Number of threads available to process messages from the queue. Determines the minimal number of threads available to process messages | 10 |
| pool-size | no | Number of threads available to process messages from the queue. Determines how many messages can be processed in parallel | 200 |
| prefix | no | Prefix given to the threads processing messages. | default |
| shutdown-timeout | no | Wait time in seconds to allow in-flight threads to gracefully finish processing before forcing them to quit | 300 |
| visibility-timeout | no | Queue visibility timeout in seconds - Messages read from the queue and kept invisible to other listeners while the node that took the message processes it. If the message is not deleted before the timeout the message is made available again for processing - retry in case of errors. | 120 |
| poll-wait | no | Listener wait time in seconds to read as many items from the queue as possible. | 10 |
| dlq-suffix | no | Dead letter queue suffix. DLQ is a generated name from the queue name with the suffix appended to the end. | `-dlq` |
| retry | no | Queue retry policy. How often is the message put for retry on the queue before it goes to DLQ. Restrictions: SQS requires at least one retry.Kafka may have no retries or up to 5 retries. | 2 |
| max-allowed-pull-size | no | Max number of allowed messages to pull from the queue. | 10 |
| props | no | Additional listener configuration. Connect SDK will read all configuration set under props and have them stored as a Map. Known properties: `retryIntervalInSec` - Used to specify the retry interval for Kafka | n/a |
Kafka Listener Configuration
Kafka is a distributed message broker that can be utilised as a messaging queue for SDK listeners. The SDK provides a seamless experience for listeners to subscribe to different message brokers through configuration if the correct SDK library is available.To configure the Kafka brokers with the SDK, use an environment variable`KAFKA_BROKERS` to specify the location of the brokers. The default value is set to `localhost:9092`.Every listener requires at least two topics, one as the main topic to receive the incoming messages and another as a dead letter queue for failed messages. If the retry policy is configured, then additional topics are required to the amount of the retry specified. The SDK expects the following naming convention for the topics, which the Kafka administrator must create, as the SDK will not automatically create them.| Topic types | Listener Configuration sample | Expected topic names |
| Main topic | name = notification | notification |
| DLQ topic | dlq-suffix = -dlq | notification-dlq |
| Retry topics | retry = 2 | notification-retry-1notification-retry-2 |
- Both listeners work with a thread pool, but the main difference is that SQS constantly pulls messages from the queue and processes them if threads are idle in the pool. On the other hand, Kafka works with batches, reads X messages from the topic, and is only capable of reading more messages once the first batch has completed processing.
- Kafka requires additional topics to support its retry policy
- Messages processed from SQS are removed from the queue, whereas in Kafka, they remain there after processing. Note that Kafka is not an event store, and selectively reprocessing old messages is not possible.
Retry mechanism:
Kafka doesn’t have a retry mechanism inbuilt like AWS SQS, and to achieve a similar behavior, SDK implements its own retry policy by using additional topics. The diagram below illustrates how messages can be forwarded to the different topics of a listener.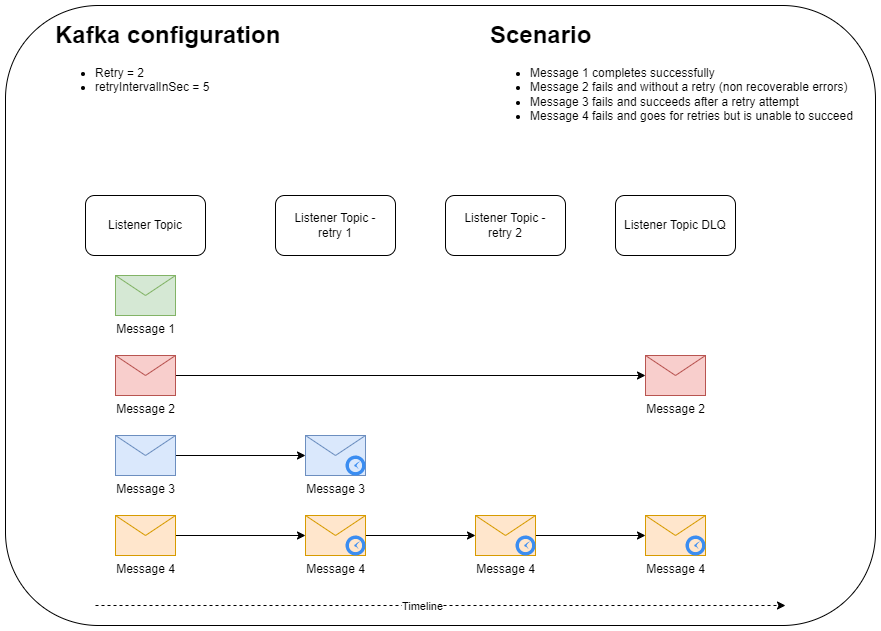 Each Kafka listener configured with a retry policy will work with a pair of listeners. The first listener is dedicated to processing messages from the main topic, while the second listener will subscribe to all retry topics. The main topic listener will never stop processing messages. The retry listener will regularly pause the subscriptions to allow the retry interval time to elapse and resume when the time is due to process the messages waiting for a retry.
Each Kafka listener configured with a retry policy will work with a pair of listeners. The first listener is dedicated to processing messages from the main topic, while the second listener will subscribe to all retry topics. The main topic listener will never stop processing messages. The retry listener will regularly pause the subscriptions to allow the retry interval time to elapse and resume when the time is due to process the messages waiting for a retry.Job Scheduler Configuration
Connect SDK doesn't have an internal scheduler, and it depends on external systems to trigger an HTTP request for a job to be executed as described below.1POST https://<domain>/api/v1/fluent-connect/scheduler/add/<fluent-account>/<fluent-retailer>/<job-name>`connect-sdk-core-aws` provides the `message-queue` mode, for example. The configuration below tells the SDK which job scheduler service to use.1job-scheduler:
2 job-scheduler-type: "message-queue"- fluent-account: Fluent account name
- fluent-retailer: Fluent retailer id
- job-name: The name of the handler that will execute the job
1POST https://localhost:8080/api/v1/fluent-connect/scheduler/add/cnctdev/1/batch-inventory-sync- A job cannot have multiple instances running simultaneously
- Retrieves the job configuration from Fluent settings.
- Calculate a date range (from-to datetime) the job may use during its execution.
- Execute the actual job.
- Persist the calculated date range as part of the job configuration for the next execution.
- Connect SDK runs at UTC time.
- Runtime configuration - More frequently updated properties that control the job behavior.
- Built time configuration - Properties that limit or give a purpose to the job that end user should modify.
Runtime configuration
- Kept at Fluent as settings
- The configuration key of a job is determined dynamically by taking the configuration
`job-scheduler.config-prefix`and appending the job name at the end. The SDK`job-scheduler.config-prefix`default template is:`fc.connect.<my-sample-connector>.batch.<job-name>`
`props`. The date `previousEndDate` is not mandatory. Whenever there is no valid date set at `prev`’s current datetime (in UTC). The calculated date range used by the job is also saved at lastRun.param.start and `lastRun.param.end` - note the correlation of `lastRun.param.end` and `previousEndDate`.1{
2 "previousEndDate": "2021-09-22T03:00:00Z",
3 "props": {
4 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
5 },
6 "lastRun": {
7 "param": {
8 "start": "1970-01-01T00:00:00Z",
9 "end": "2021-09-22T03:00:00Z",
10 "props": {
11 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
12 }
13 },
14 "jobStart": "2021-09-22T03:00:00Z",
15 "jobEnd": "2021-09-22T03:05:00Z",
16 "status": "SUCCESSFUL"
17 }
18}`previousEndDate` is used as the start date `lastRun.param.start` and a new date is set for both `lastRun.param.end` and `previousEndDate`.1{
2 "previousEndDate": "2021-09-22T02:00:00Z",
3 "props": {
4 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
5 },
6 "lastRun": {
7 "param": {
8 "start": "2021-09-22T03:00:00Z",
9 "end": "2021-09-23T02:00:00Z",
10 "props": {
11 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
12 }
13 },
14 "jobStart": "2021-09-23T02:00:00Z",
15 "jobEnd": "2021-09-23T02:05:00Z",
16 "status": "SUCCESSFUL"
17 }
18}1{
2 "customDateRange": {
3 "start": "2021-04-22T00:00:00Z",
4 "end": "2021-04-23T00:00:00Z"
5 },
6 "previousEndDate": "2021-09-22T02:00:00Z",
7 "props": {
8 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
9 },
10 "lastRun": {
11 "param": {
12 "start": "2021-09-22T03:00:00Z",
13 "end": "2021-09-23T02:00:00Z",
14 "props": {
15 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
16 }
17 },
18 "jobStart": "2021-09-23T02:00:00Z",
19 "jobEnd": "2021-09-23T02:05:00Z",
20 "status": "SUCCESSFUL"
21 }
22}`previousEndDate` remains as it previously was so the job resumes its normal operation.1{
2 "previousEndDate": "2021-09-22T02:00:00Z",
3 "props": {
4 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
5 },
6 "lastRun": {
7 "param": {
8 "start": "2022-04-22T00:00:00Z",
9 "end": "2022-04-23T00:00:00Z",
10 "props": {
11 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
12 }
13 },
14 "jobStart": "2021-09-24T02:00:00Z",
15 "jobEnd": "2021-09-24T02:05:00Z",
16 "status": "SUCCESSFUL"
17 }
18}`executionStart` is added to indicate the job is running, and it is removed when the job is completed.1{
2 "previousEndDate": "2021-09-22T02:00:00Z",
3 "executionStart" : "2021-09-24T02:00:00Z",
4 "props": {
5 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
6 },
7 "lastRun": {
8 "param": {
9 "start": "2022-04-22T00:00:00Z",
10 "end": "2022-04-23T00:00:00Z",
11 "props": {
12 "fluentNetworkRef": "BASE_67"
13 }
14 },
15 "jobStart": "2021-09-24T02:00:00Z",
16 "jobEnd": "2021-09-24T02:05:00Z",
17 "status": "SUCCESSFUL"
18 }
19}| Property | Description |
| customDateRange | Optional date range a user can set to override the jobs current `previousEndDate`. This is only used once and gets removed after a successful execution. |
| customDateRange.start | Custom user date range start datetime in UTC. |
| customDateRange.end | Custom user date range end datetime in UTC. |
| previousEndDate | Used to keep track of the last execution date. This drives how the SDK calculates the next date range execution. Whatever the value is set here, this is used as the next start date. If this is missing or invalid, epoch is as the start date. The end date is always the current time the job is executed. |
| props | Optional job settings. |
| lastRun | Keeps a copy of the last execution parameters, date range used as well as job execution times. |
| lastRun.param.start | Last execution date range start in UTC. |
| lastRun.param.end | Last execution date range end in UTC. |
| lastRun.param.props | Last execution props. |
| lastRun.jobStart | Last execution date time the job start running in UTC. |
| lastRun.jobsEnd | Last execution date time the job finished running in UTC. |
| lastRun.status | Last execution status of how the job finished: FAILED / SUCCESSFUL. |
Kafka Limitations
When using a Kafka topic to queue job requests from a scheduler, it's important to consider that Kafka works differently from SQS. When the SDK reads messages from the job topic using Kafka, it will take the available job requests and start processing them. If new job requests arrive while the first set is still being processed, then these will remain queued until the SDK completes the first set and is able to take the queued jobs. A queued job time to live is heavily coupled with how frequently the SDK pulls the topic and the lowest frequency allowed is 1 minute. It is not possible to guarantee that the first job requests will complete processing before the second set of job requests expires. When job requests expire in the topic, they get discarded and are moved to the DLQ. This means the schedule job is not executed and it will have to wait until the scheduler issues another request for its execution.Build configuration
The first level of a job configuration is at the class where the job is written through the`HandlerInfo` annotation.1@HandlerInfo(
2 name = "InventorySyncJob",
3 route = "batch-inventory-sync",
4 description = "Sync inventory positions from Fluent to Commercetools",
5 props = {@HandlerProp(key = "page-size", value = "500")}
6)`InventorySyncJob` and creates a new route also setting new properties. With the configuration below, it is possible to execute the same job through different routes with different properties.1 routes:
2 job:
3 - route: "batch-inventory-sync"
4 handler-name: "InventorySyncJob"
5 props:
6 page-size: 1000
7 - route: "custom-inventory-sync"
8 handler-name: "InventorySyncJob"
9 props:
10 page-size: 200
11 another-property: "some value"Cache Configuration
ConnectSDK uses spring cache to store some data in memory and the table below lists the standard caches from SDK.| Cache Name | Description | Default Expiry in Seconds |
| fluent-api-client | Fluent API Client cache | 300 |
| account-mapping | Fluent account mapping cache. This is often used to map a Fluent account to external systems or vice versa | 300 |
| account-mappings | Fluent account mapping cache. This is often used to map a Fluent account to external systems or vice versa | 300 |
| account-configuration | Configuration (Fluent settings) cache | 300 |
| fluent-auth-token-context | Handler context cache from a Fluent Auth token | 300 |
| api-key-context | Handler context cache from a SDK API Key | 300 |
1fluent-connect:
2 cache:
3 caffeine:
4 - name: "fluent-api-client"
5 expiryInSeconds: 600
6 - name: YourNewCache
7 expiryInSeconds: 6001@Cacheable(cacheManager = cacheManager = CacheConfiguration.SDK_CACHE_MANAGER, cacheNames = "YourNewCache")Product Availability
Feature Configuration
| Property | Description | Default |
| fulfilment-option.enabled | Enables the product availability endpoint. If set to false the endpoint is not available and the request will result in a 404 response. | true |
| fulfilment-option.logging.enabled | Logs extra information on the request, response, and execution time of each enrichment step. Not recommended for production environments. | false |
API Key Configuration
API Keys are configured directly at the Secret Manager just like any other credential used by the SDK. API keys are specific for a Fluent account and therefore must be configured using the following secret key template:`fc/connect/{connector-name}/{fluent-account-name}/api/fluent-account/api-keys`. Note that `connector-name` and `fluent-account-name` must be updated with the correct values before using the key above.A token has the following properties:- API Key size: must contain at least 16 characters.
- Duplicate keys: Must be unique. Duplicate tokens are deemed invalid by the SDK and disregarded.
- Expiry: May or may not have an expiry. Tokens without an expiry will always be valid. The expiry date-time must be in UTC format as shown below.
- Caching: keys are cached by the SDK. Modifying an API key configuration may not have an immediate effect.
- Multi-retailer: It's possible to have any number of retailers with any number of keys for each retailer.
1{
2 "api-keys": [
3 {
4 "retailer": "1",
5 "username": "fluent-username-1",
6 "password": "ZMCZZZ",
7 "keys": [
8 {
9 "key": "1283712983721983",
10 "expiry": "2020-12-30T20:28:07.00Z"
11 },
12 {
13 "key": "3333332222222222"
14 }
15 ]
16 },
17 {
18 "retailer": "34",
19 "username": "fluent-username-34",
20 "password": "ZMCFFF",
21 "keys": [
22 {
23 "key": "2222333344445555"
24 }
25 ]
26 }
27 ]
28}1curl -X 'GET' \
2'http://localhost:8080/api/v1/fluent-connect/api-key' \
3-H 'Authorization: ApiKey 1283712983721983'
4-H 'fluent.account: CNCTDEV'Spring actuators
The SDK is built with Spring Framework, and it bundles a couple of custom actuators on the top of the default ones. The list of enabled actuators in the SDK can be found at bootstrap.yml file. To view the list of actuators active, see http://localhost:8080/actuator.To learn more about actuators, please see Spring Boot Actuator Web API Documentation.This is the default SDK settings for actuators.
1management:
2 endpoints:
3 web:
4 exposure:
5 include: health, info, caches, scheduledtasks, sdkhandlers, sdkroutes